A stock is a type of security that gives stockholders a piece or a share of ownership in a company. Stocks also are called “equities,” and the words “stock” and “share” are usually used interchangeably, since a share is the metric for a unit of stock. Companies sell goods and services and since their stock prices are tied to their underlying profit and future earnings potential, stocks have the potential to continue to grow over time as companies grow their revenue and profits. Stocks are bought and sold on a stock exchange through a brokerage.
Here’s an example of Apple Inc. (AAPL) stock price over time. You can see how their revenue and profit grew over the same period and the impact on an initial $100 investment in the same stock over that period:
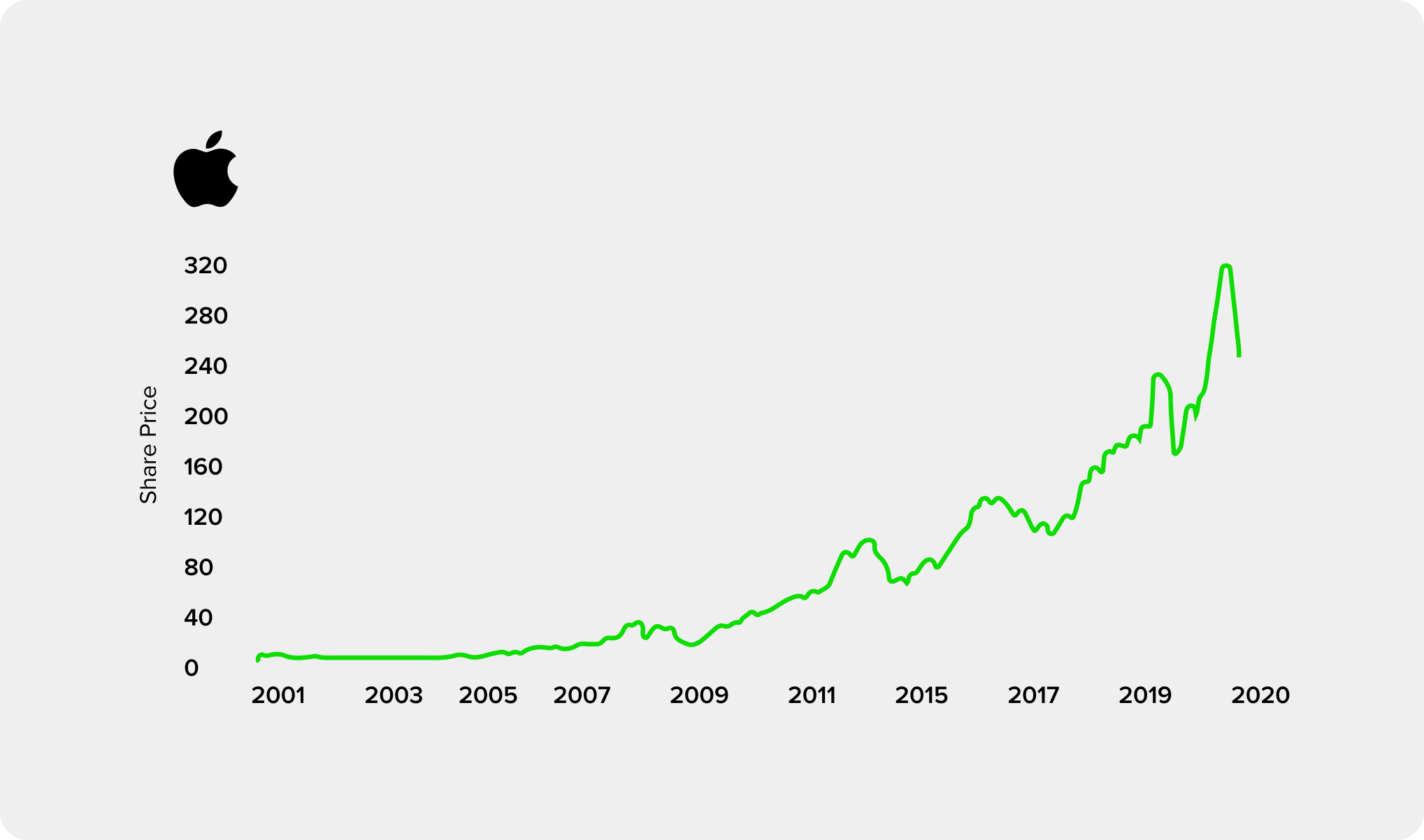
The price of a stock is primarily driven by a company’s profits and investors’ confidence in a company’s profit potential but can be impacted both negatively and positively by several other factors as well. Being volatile and unpredictable in nature, stock prices can increase or decrease on any given day. As an investor, if you sell your shares on a day when the stock price is above what you paid for it, then you will make a profit. The opposite can also happen – if you sell your shares when the stock price is below what you paid for it, then you will lose money.
Prominent investors like Warren Buffett or Jack Bogle recommend that you ‘buy and hold’ stocks for the long term to benefit from their long-term value. Here’s what Warren Buffett has been quoted as saying in the past about owning stocks:
"Put together a portfolio of companies whose aggregate earnings march upward over the years, and so also will the portfolio’s market value,” Buffett wrote in his 1996 letter to shareholders. “If you aren’t willing to own a stock for ten years, don’t even think about owning it for ten minutes.
Why do people buy stocks?
There are various reasons why investors buy stock, including potential for growth (capital appreciation), dividend payments and the ability to vote and influence company decisions – depending on the type of stock bought. Investors buy shares when they think that a certain company will be profitable, enabling them to potentially obtain a return on investment on their stock purchase. Investors buy and sell stock based on how much they think the stock will be worth in the future.
Ownership is determined by the number of shares a person owns relative to the number of a company’s outstanding shares. For example, if a company has 1,000 shares of stock outstanding and one person owns 100 shares, that person would own and have claim to 10% of the company's assets and earnings.
Owning stock gives you the right to vote in shareholder meetings, receive dividends (the company’s profits), and gives you the right to sell your shares to someone else.
What is the difference between common stock and preferred stock?
There are two main kinds of stock – common stock and preferred stock. Common stock has its advantages, like how it entitles its owners to vote at shareholder meetings and receive dividends. On the other hand, preferred stockholders don’t usually have voting rights, but they receive dividend payments before common stockholders and have priority over common stockholders if a company goes bankrupt and its assets are liquidated.
When does a company issue common stock vs preferred stock?
Many companies choose to issue preferred stock over common stock because companies can get more funding with preferred shares since many investors are looking for more consistent dividends. Additionally, preferred stock allows companies to keep their debt-to-equity ratio lower and it gives less control to outsiders.
Why does a company issue stock?
Companies issue stock to raise funds for a variety of reasons, such as scaling up, expansion, launching new products and new business ventures. Generally, only public companies can issue stock on a stock exchange. Once a private company first offers its shares to the public – called an Initial Public Offering – then investors can begin buying shares of that company’s stock.
Dependent on how much capital a company is looking to raise, it can issue additional shares through a secondary offering. As the company grows and earns more profits, it can choose to pay dividends to its shareholders, or reinvest its profits back into the company, therefore increasing its market value and the value of the stock.
A company also has the option of repurchasing its shares – this can bump the stock price up, therefore increasing its market value. There are a few reasons a company might buyback shares. It could be because the company believes the market has discounted its shares too steeply, to invest in itself or to improve its financial ratios. When a company buys back its shares, the ownership of each investor increases because there are less shares available.
What is market cap?
Market capitalization – otherwise known as market cap – refers to the total dollar market value of a company’s outstanding shares of stock, or how much a company is worth as determined by the stock market. It is calculated by multiplying the total number of a company’s outstanding shares by the current market price of one share.
For example, at the time of this writing, Apple’s market cap is $1.705 trillion. With its shares trading at $393.43, that means that Apple has approximately 4.33 billion shares outstanding. If an investor owns 10,000 shares of Apple, they have .0002% ownership of Apple.
What makes a stock price go up or down?
There are many forces that can drive stock price up or down. Fundamental factors that can drive a stock price up or down include its earnings and valuation – essentially the potential future earnings an investor can make on a certain stock.
Companies are also under unavoidable influences and market factors that influence its stock price such as cost of material, changes in technology and labor costs. Other factors that can affect a company’s stock price include bad publicity, changes in leadership and trade policy.
When investors start to lose confidence and think that their shares in a company will start to lose profitability, investors may start to sell their stocks in hopes of making a profit. This drives the stock price down, and therefore the market value of a company.
Since there is such a large amount of risk and volatility when investing in stocks, we recommend diversifying your portfolio with a combination of different asset types to help offset those risks.

